
Published in:
Web Designing
7 Key Principles of Accessibility and Inclusive Design for Websites

Accessibility and inclusive design for websites are key principles that ensure that all users, regardless of language, culture, location, ability or disability, can access and use a website. This is achieved by designing websites with features that accommodate the needs of different user groups.
Why Web Accessibility?
Web Accessibility is an important part of creating an inclusive web design. It involves making sure that websites are usable by everyone, regardless of any disabilities they may have. By taking into account the needs of people with disabilities, accessibility allows them to access and use a website just as everyone else does.Having an accessible website also makes for a better user experience for everyone. Websites that are designed inclusively take into account different types of user input, such as voice commands or special keyboards. This ensures that the site is easy to use across many different platforms and devices, making it more appealing to potential users. Additionally, having an accessible website can help improve search engine optimization (SEO) rankings since search engines recognize sites with better usability and performance ratings.For example, good accessibility may include providing subtitles or captions on videos so they can be enjoyed by those who are hard of hearing. Inclusive design ensures that everyone has an equal chance to access information and services online. This includes providing alternative text for images, avoiding non-essential animations, and ensuring all content is readable in any font size. Good accessibility also requires consistent navigation and clear labels as well as making certain more complex content is broken down into smaller chunks for easier understanding. By following these principles during web development we can make sure that everyone can benefit from our website equally.
1. Design for accessibility:
Design with accessibility in mind and make sure the website is accessible to all users, regardless of disability or impairment.
- Design web page with clear and simple navigation in mind so it is easy to use by all users.
- Ask your web designer to choose font sizes, colors, and other design elements carefully to ensure they are accessible to people who have difficulty seeing or distinguishing colors.
- Use alt-text for images so that screen readers can read them out loud for visually impaired users.
- Include closed captioning on videos and audio files for deaf or hard of hearing users.
- Add skip navigation links at the top of the page so people using a keyboard can quickly access the main content without having to tab through the entire navigation menu.
- Make sure your site is compatible with assistive technologies like voice recognition software, screen readers, and magnifiers used by some disabled users.
- Provide alternative means of providing information such as transcripts for video content and text alternatives for audio files for people who cannot access that type of content due to disability or impairment.
- Test your website in different web browsers and devices to make sure all features are working properly on all platforms.

2. Create clear navigation:
Create a clear and intuitive site structure so that users can easily navigate and find the content they need.
- Start with a simple and uncluttered homepage that displays the most important information in an organized way.
- Utilize a navigation menu to allow users to easily find their way around the website. This should be placed at the top of each page and clearly labeled to indicate what sections are available.
- Break down content into categories and subcategories, making it easy for users to find what they’re looking for quickly.
- Include a search box on each page so that users can type in keywords or phrases and find relevant results instantly.
- Add breadcrumbs so that users can easily trace their steps back to where they started from if they get lost or confused.
- Make sure that all links are clearly labeled, so that users know exactly where clicking them will take them before they click them.
- Provide clear instructions for filling out forms and other interactive elements, as well as helpful feedback when errors occur, so that users don’t get stuck or frustrated while using the website.
3. Ensure readability:
- Use simple language and avoid jargons. Small sentences also help people to understand Website contents easily.
- Utilize translation tools to make content accessible in multiple languages. Google Translation is a great tool and it can be easily integrated by just adding a small code of Java script provided by google.
- Increase font size for easier readability.
- Make sure there is good contrast between text and background colors, as well as between headers and body text.
- Visual design also increase the readability. Make sure your UX design is graphically rich as well easy to use.
4. Allow customization:
Your Web design should Offer ways for users to customize their experience so they can adjust things like font size, color scheme, etc., to suit their needs.
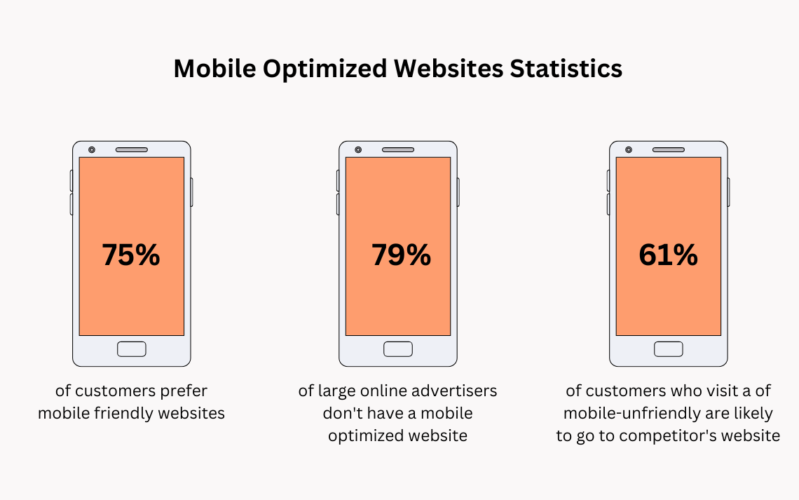
5. Optimize for mobile devices:
Make sure your website looks great on mobile devices and works well with touch interfaces.
- Use Responsive Design: A responsive website design automatically adjusts the layout of your website to fit any size screen. This ensures that your website looks great across all devices, from desktops to tablets and mobile phones.
- Optimize for Touch: Make sure that all elements on your website are easy to use with a touch interface by increasing the size of buttons and links, making sure they have enough space between them, and adding tap targets.
- Minimize Load Times: Mobile users are often on slower connections so it’s important to ensure that your website loads quickly on these devices. Optimize images, minify code, and utilize caching whenever possible to reduce load times.
- Reduce Scrolling: Many mobile users find scrolling tedious so try to minimize the amount of vertical scrolling needed on your site by reducing content length or breaking it up into multiple pages if possible.
- Consider Usability: Think about how a user will interact with each page of your site and make sure everything is intuitive and easy to use on both desktop and mobile devices.
6. Provide alternative access methods:
Make sure there are alternative ways of accessing content such as keyboard navigation, voice commands, etc., for those who are unable to use a mouse or other input device.
7. Test your website regularly:
Regularly test your website using automated tools as well as manual testing with people from different backgrounds and abilities to ensure its usability and accessibility for everyone who visits it.
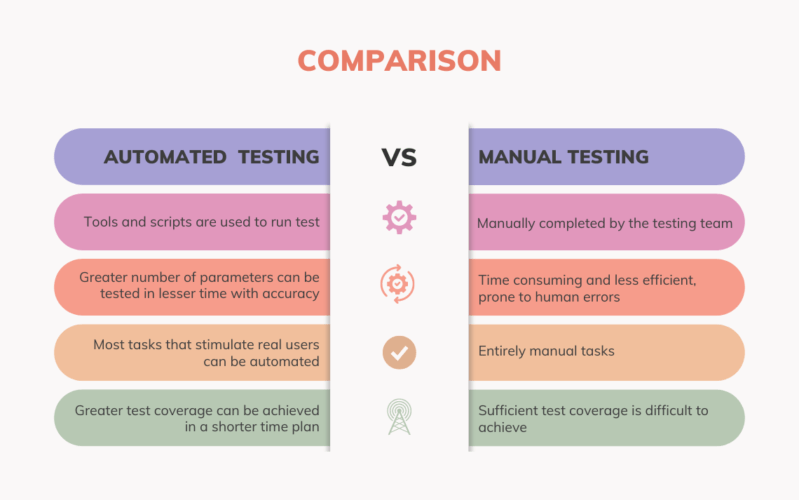
- Automated tools for website testing are becoming increasingly popular among web developers and testers. These tools automate the process of testing a website, making it faster and more efficient. Automated tools can check for broken links, evaluate page loading times, verify page content, detect errors and check for compatibility with different browsers. They can also be used to monitor website performance over time to ensure that it is functioning properly. These automated tools can even alert developers when changes to the code or functionality occur so that they can make necessary adjustments. In addition, these tools can be used to generate detailed reports on website performance which allow developers to identify potential issues and fix them quickly.
- Manual web testing is a process of manually testing the functionality and user experience of a website. This involves testing different aspects such as navigation, content, performance, compatibility, security and usability. It requires a tester to have an in-depth knowledge of the website structure and its navigation paths to be able to effectively test it. Manual web testing also includes verifying the accuracy of information on each page and ensuring that all links are working properly. A tester needs to be knowledgeable about HTML, CSS and JavaScript in order to be able to detect any potential errors or bugs that may arise during the process. Manual web testing is an important step in ensuring that a website functions properly before it is launched to its intended audience.
Final thoughts
By following these 7 key principles of accessible and inclusive design, we can make sure that everyone has an equal chance to access information and services online. This includes providing alternative text for images, avoiding non-essential animations, and ensuring all content is readable in any font size. Good accessibility also requires consistent navigation and clear labels as well as making certain more complex content broken down into smaller chunks for easier understanding.



